Programme: Master of Library & Information Science
Course: MLIS-09: Research Methodology
Target group: Master's students & Research Scholars
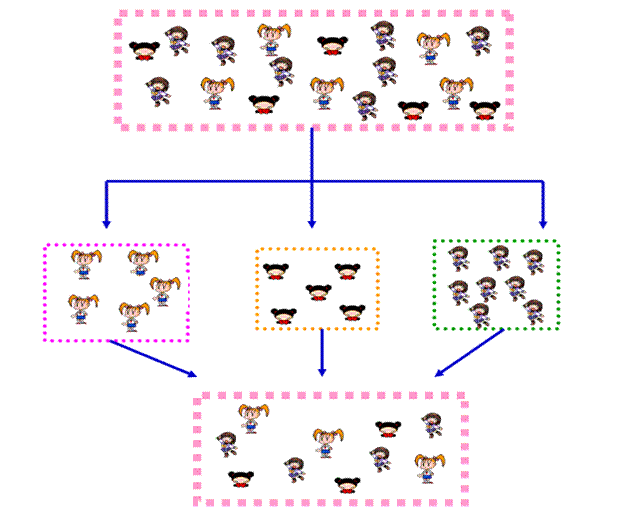
Cluster Sampling:
In this method the total population is divided into some sub-divisions which are termed as clusters using simple random method. All the units in each cluster are surveyed. The cluster should be as small as possible. When the cluster is small will be easy to study and it saves time and money. The number of units in each cluster should be the same.
If the clusters are many, then the probability and representativeness of the sample is affected. The results will be less accurate if the number of sampling units in each cluster are not same.
Multi-Stage Sampling:
This method is generally used in selecting a sample from a very large area. Multi-stage sampling refers to the technique which is carried out in various stages. The entire population is regarded to consist of number of primary units. The primary units are again composed of secondary units which further consist of third stage units and so on until the researcher ultimately obtains the desired sample. At each stage random sampling techniques are used. The sample size may be proportional or disproportional.
This method is particularly useful in surveys of under developed areas where up to date sample frame is not available. However, errors are likely to be large in this method compared to other methods.
Activity
1. Compare the following figures and bring out the major difference between Stratified sampling and clouster sampling methods.
 |
| Stratified Random Samling |
 |
| Cluster Sampling |
